Analysis of Alleged Breaches of Care in Obstetrics

Overview
This analysis examines 103 distinct alleged breaches of the standard of care, drawn from 45 medicolegal cases spanning 2015-2025 (median year: 2022). For clinicians and quality teams, this analysis identifies the clinical domains most frequently associated with alleged breaches, offering a roadmap for targeted quality improvement initiatives.
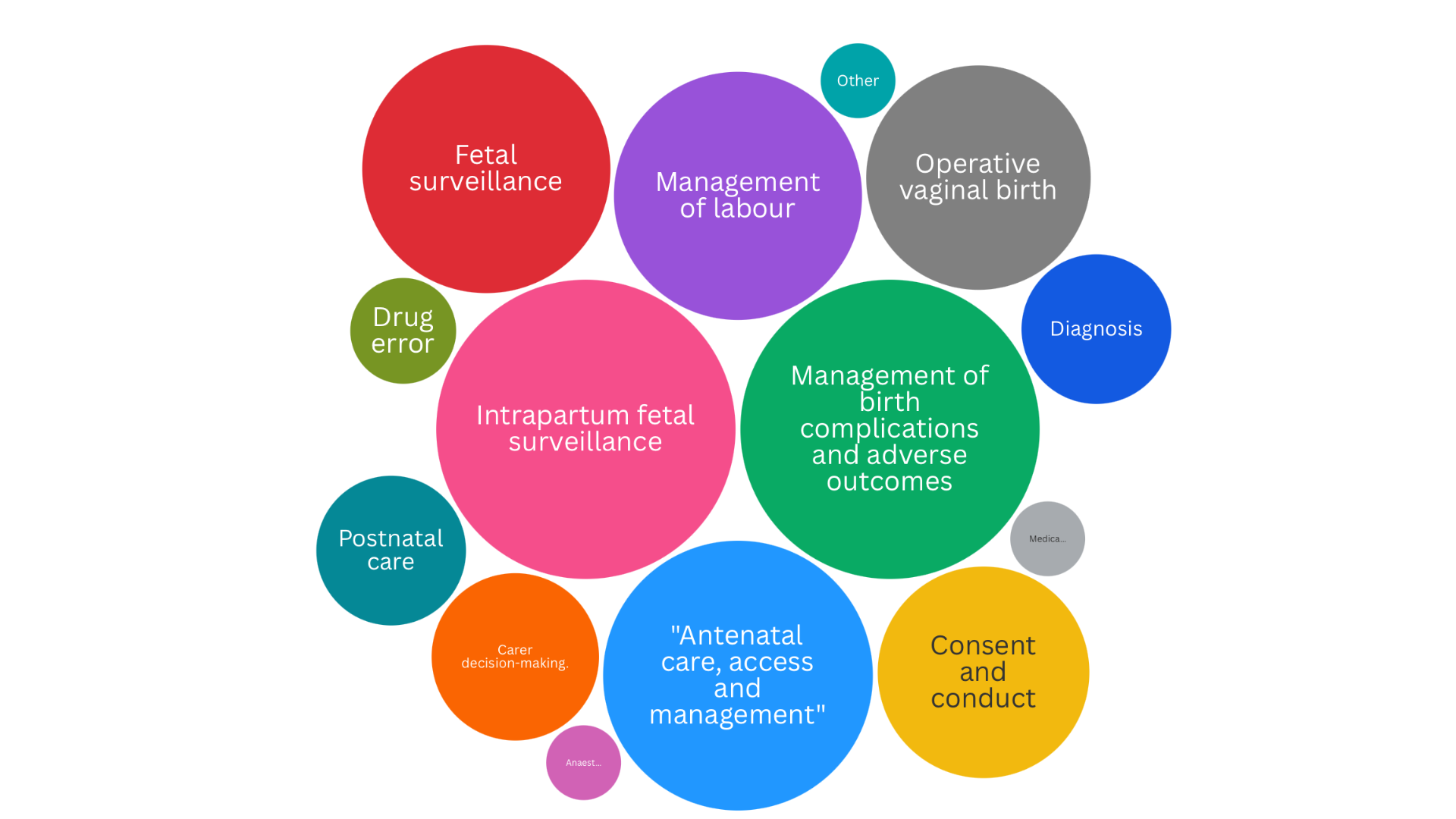
Key Findings
The distribution of alleged breaches across clinical domains reveals clear patterns:
- Intrapartum fetal surveillance: 16.7%
- Management of birth complications: 16.7%
- Antenatal care, access and management: 13.5%
- Fetal surveillance (antenatal): 11.5%
These findings underscore the critical importance of robust CTG interpretation skills, clear escalation pathways, and structured management of intrapartum complications.
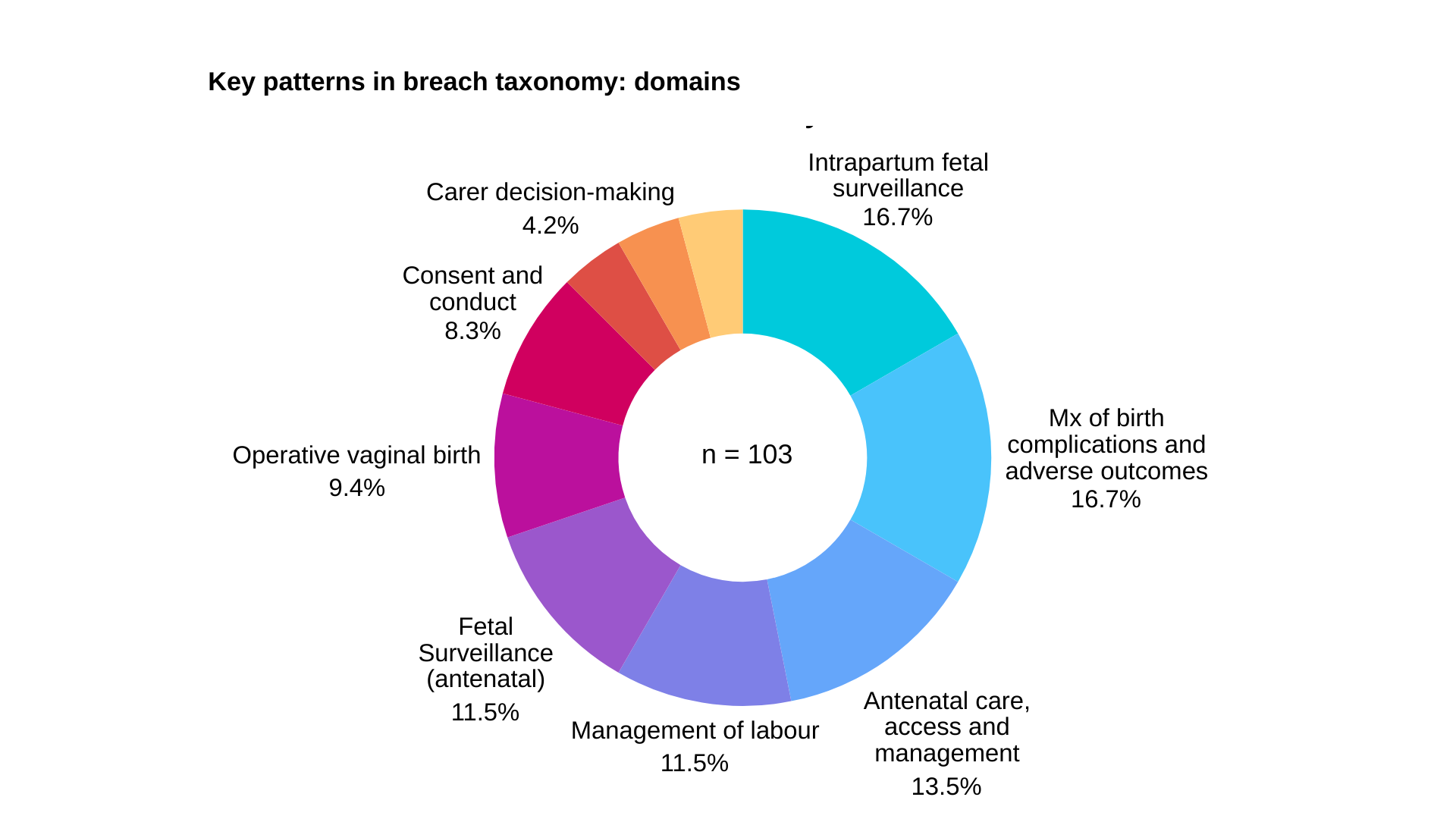
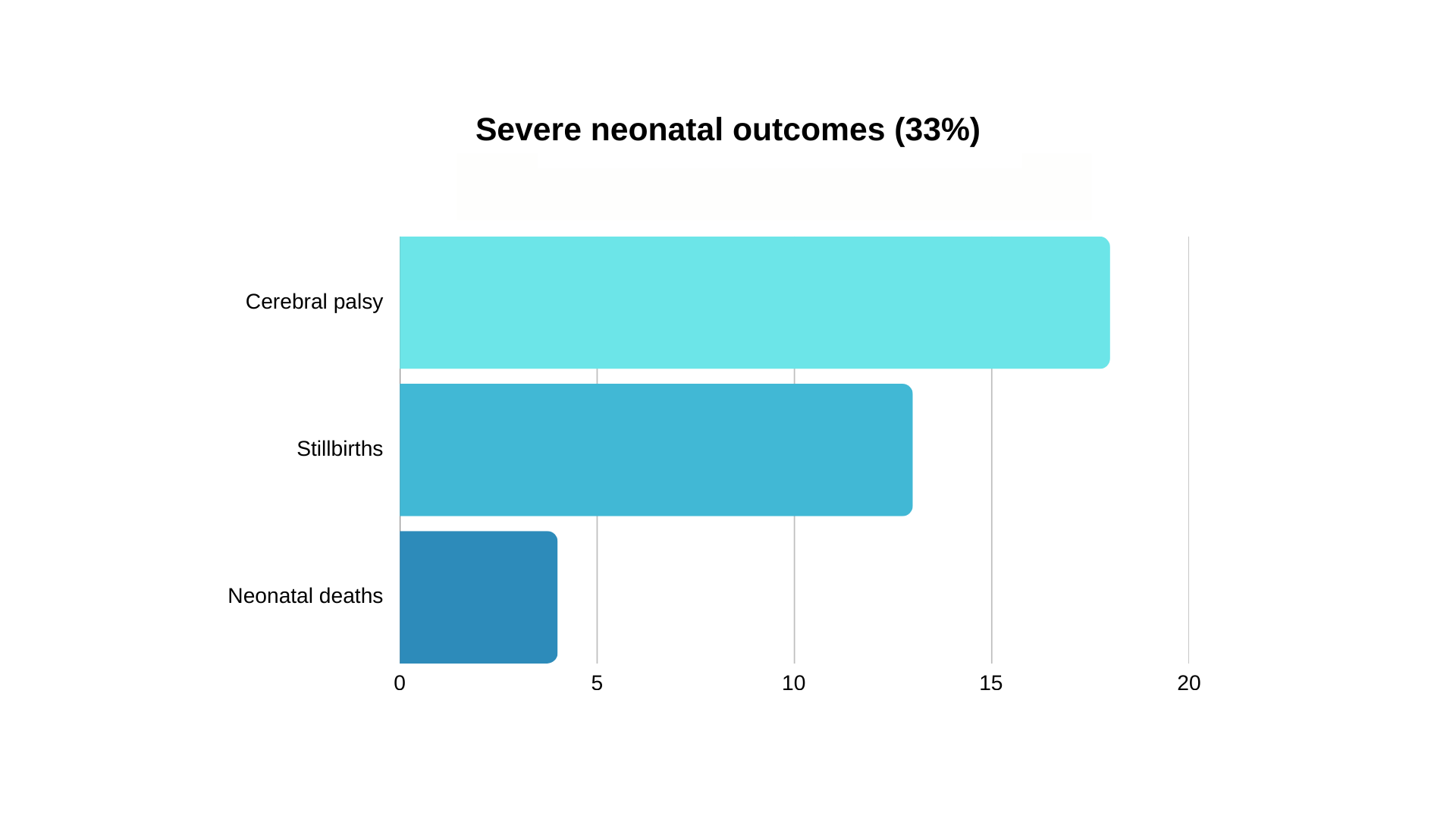
Severe Outcomes
Of the cases involving cerebral palsy, 88.9% were related to intrapartum care—highlighting the critical window during labour where timely intervention can prevent catastrophic outcomes.
Illustrative Case: CTG Misinterpretation
A common and devastating pattern involves the misinterpretation of cardiotocography (CTG) traces. In one representative case, a 28-year-old primigravida presented in labour at 40+2 weeks.


Following epidural placement, monitoring was switched to continuous CTG.
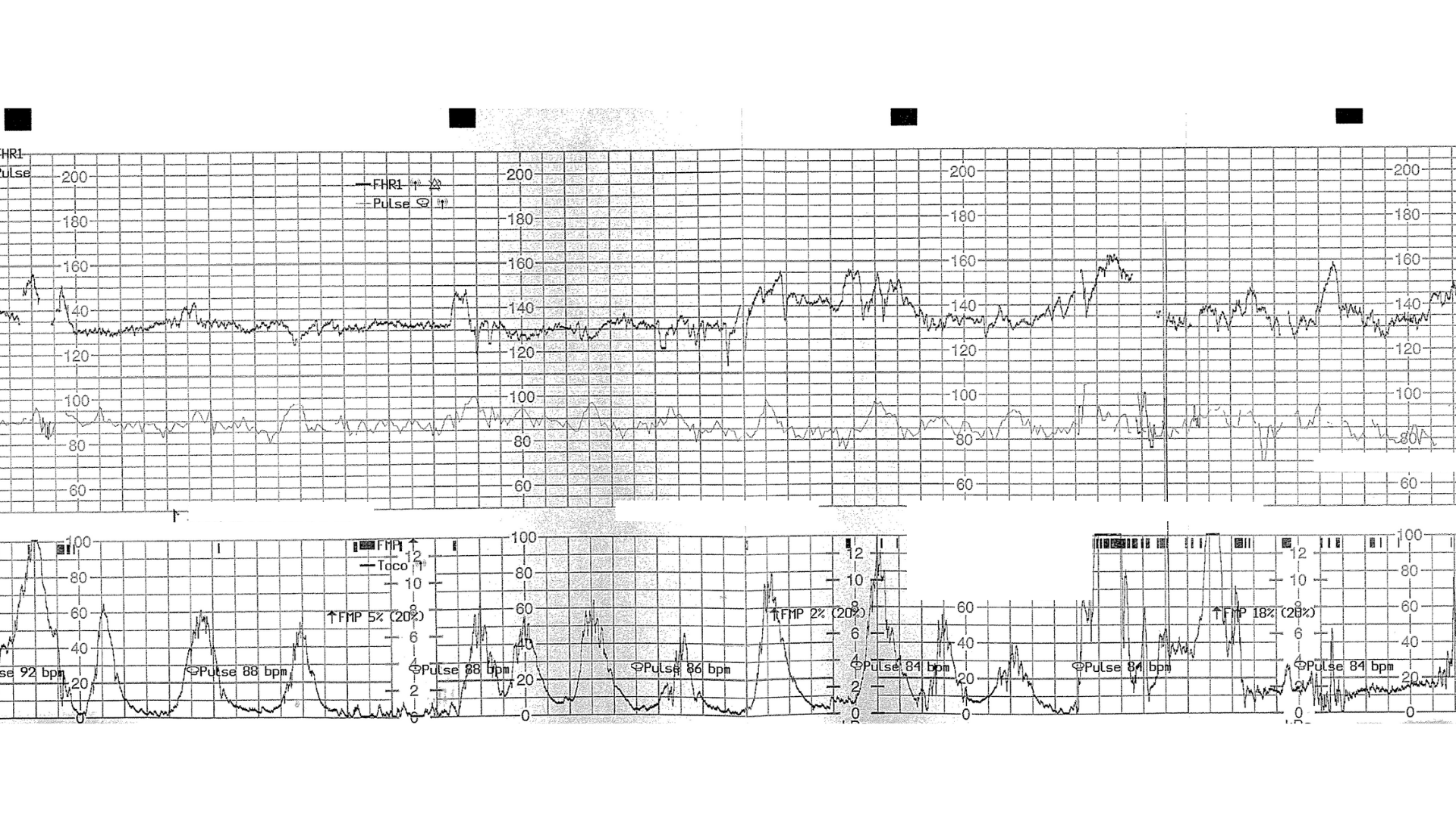
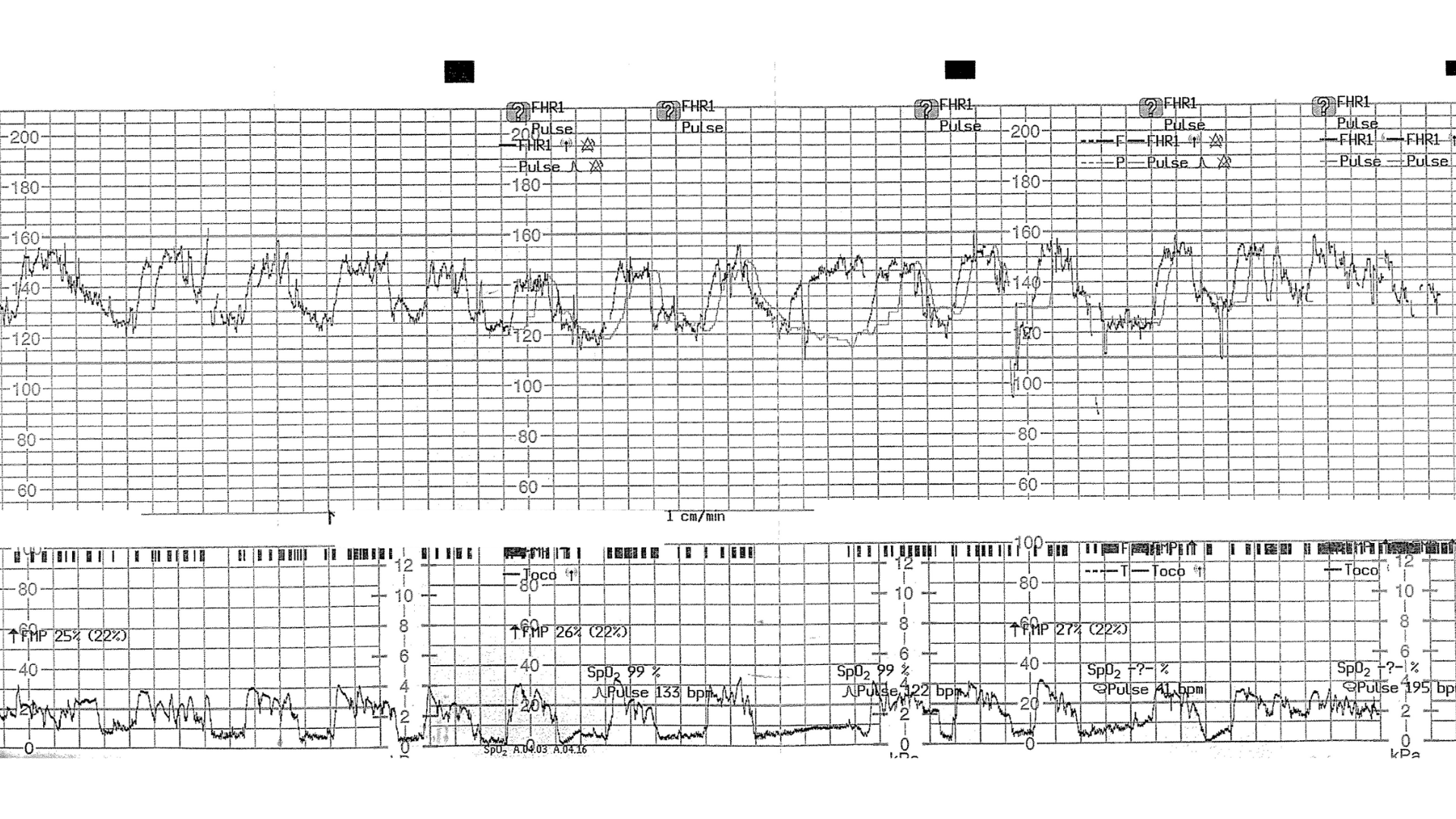
The CTG trace was actually maternal heart rate artefact, masking fetal distress.
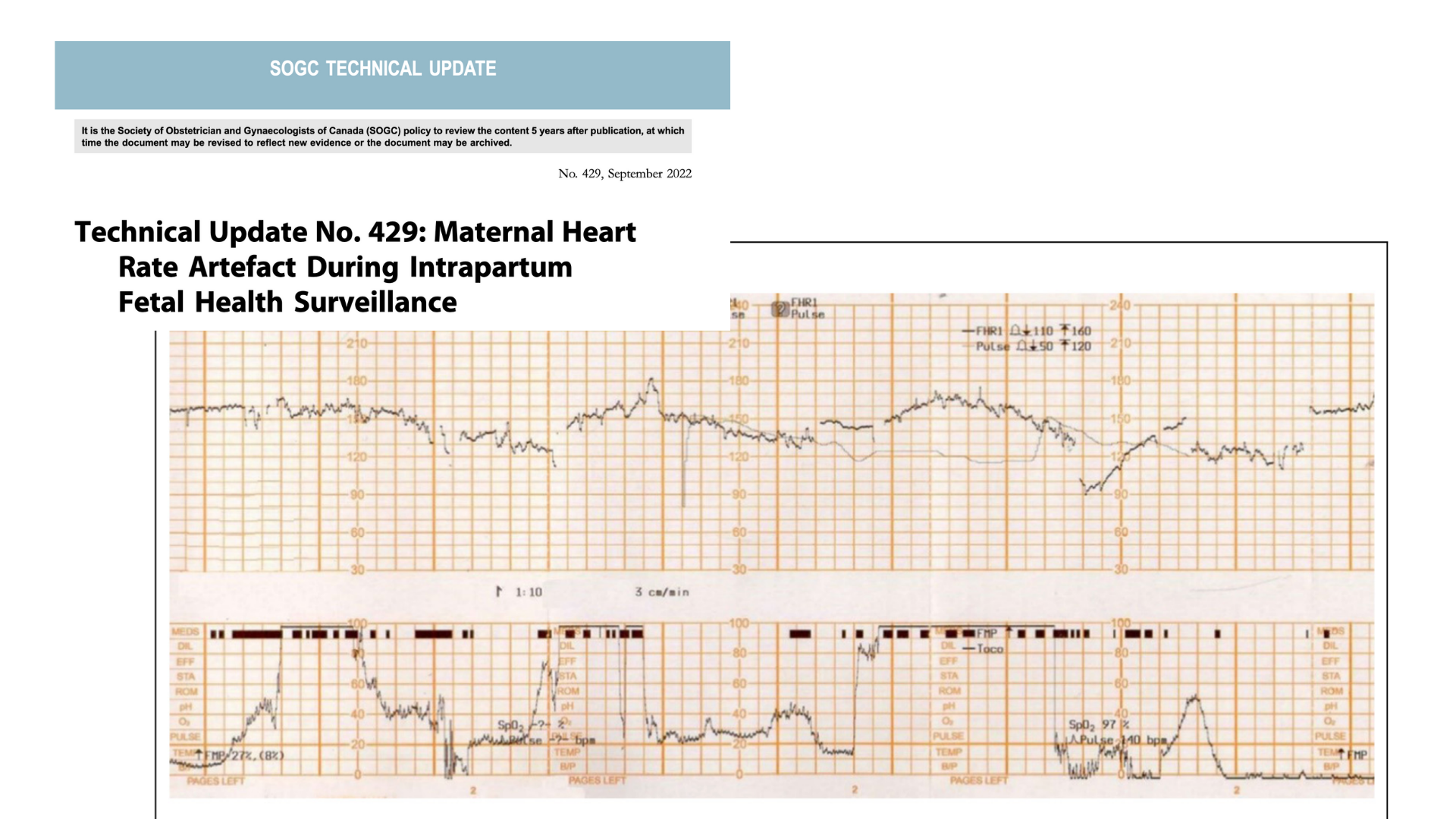

The baby required therapeutic hypothermia and sustained significant brain injury.

This case reinforces the importance of confirming fetal heart rate identity, particularly after interventions, and maintaining vigilance for maternal heart rate artefact.
Systemic Factors
Beyond individual clinical decisions, four recurring systemic themes emerged:
- Over-reliance on technology
- Failure of guideline implementation
- Inadequate communication
- Barriers to escalation